TEL
AI in Education – the question of hype and reality


Max Gruber / Better Images of AI / Banana / Plant / Flask / CC-BY 4.0
I have spent a lot of time over the past two weeks working on the first year evaluation report for the AI pioneers Web site. Evaluation seems to come in and out of fashion on European Commission funded projects. And now its in an upswing, partly due to the move to funding projects based on the products and results, rather than number of working days claimed.
For the AI Pioneers project, I have adopted a Participant oriented approach to the evaluation. This puts the needs of project participants as its starting point. Participants are not seen as simply the direct target group of of the project but will includes other stakeholders and potential beneficiaries. Participant-orientated evaluation looks for patterns in the data as the evaluation progresses and data is gathered in a variety of ways, using a range of techniques and culled from many different sources. Understandings grow from observation and bottom up investigation rather than rational deductive processes. The evaluator’s key role is to represent multiple realities and values rather than singular perspectives.
Hopefully we will be able to publish the Evaluation report in the early new year. But here are a few take aways, mainly gleaned from interview I undertook with each of the project partners.
The partners have a high level of commitment to the project. However the work they are able to undertake, depends to a large extent on their role in their organisations and the organisations role in the wider are of education. Pretty much all of the project partners, and I certainly concur with this sentiment, feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of reports and discourse around AI in education and the speed of development especially around generative AI, makes it difficult to stay up to date. All the partners are using AI to some extent. Having said that there is a tendency to thing of Generative AI as being AI as a whole, and to forget about the many uses of AI which are not based on Large Language Models.
Despite the hype (as John Naughton in his Memex 1.1 newsletter pointed out this week AI is at the peak of the Gartner hype cycle, see illustration) finding actual examples of the use of AI in education and training and Adult Education is not easy.

A survey undertaken by the AI pioneers project found few vcoati0nal education and train9ing organisations in Europe had a policy on AI. There is considerable differences between different sectors - Marketing, Graphic design, computing, robotics and healthcare appear to be ahead but in many subjects and many institutions there is little actual movement in incorporating AI, either as a subject or for teaching and learning. And indeed, where there are initial projects taking place, this is often driven by enthusiastic individuals, with or without the knowledge of their managers.
This finding chimes with reports from other perspect6ives. Donald H Taylor and Egle Vinauskaite have produced a report looking at how AI is being used in workplace Learning and Development today, and concludes that it is in its infancy. "Of course, some extraordinary things are being done with AI within L&D," they say. "But our research suggests that where AI is currently being used by L&D, it is largely for the routine tasks of content creation and increased efficiency."
If there is one message L&D practitioners should take away from this report, it is that there is no need to panic – you are not falling far behind your peers, for the simple reason that very few are making major strides with AI. There is every need, however, to act, if only in a small way, to familiarize yourself with what AI has to offer.
Donald H Taylor and Egle Vinauskaite. Focus on AI in L&D, https://donaldhtaylor.co.uk/research_base/focus-on-ai-in-ld/
Indeed, for all the talk of the digital transformation in education and training, it my be that education, and certainly higher education, is remarkably resistant to the much vaunted hype of disruption and that even though AI will have a major impact it may be slower than predicted.
Generative AI for teaching and learning

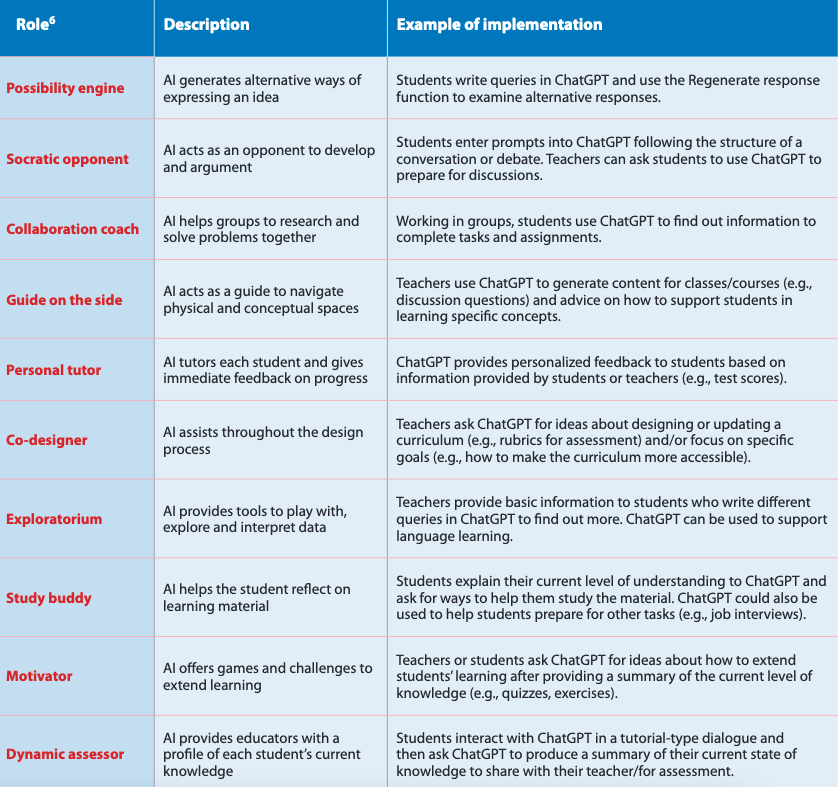
I missed this when it was published in April. But this table, is in a Quickstart Guide to ChatGPT by UNESCO which "provides an overview of how ChatGPT works and explains how it can be used in higher education. The Quick Start Guide raises some of the main challenges and ethical implications of AI in higher education and offers practical steps that higher education institutions can take." The table provides a useful summary of the different pedagogical possibilities fo using Generative AI for teaching and learning.
Top tools for Learning

Photo by ThisisEngineering RAEng on Unsplash
Jane Hart from the Centre for Learning & Performance Technologies has published the seventeenth in her annual survey of the Top 100 Tools for Learning. There were 2,022 votes in the survey drawn from both the education sector and industry. There was little change or surprise in the top three" YouTube, Google Search and Microsoft Teams. And perhaps there should be no surprise in the fourth top tool with ChatGPT leaping in from nowhere the year before. Other big winners in this years survey were Netflix, Grammarly and Tiktok. Jane explained that this year there were more votes from the education sector than last year, leading to many of the educational tools have regaining lost ground over more productivity and workflow tools on this year’s list.A proposed AI Competency Framework for teachers
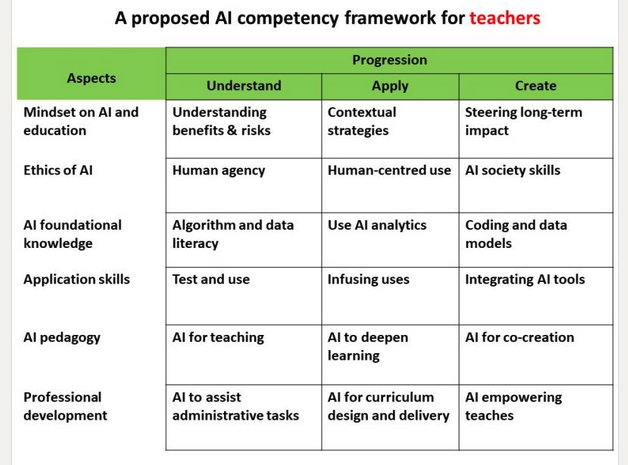
This is interesting. It is included in a LinkedIn post by Fengchun Miao, Chief of Unit for Technology and AI in Education at UNESCO.
In his post he says he is posting it for feedback and may delete it soon"


