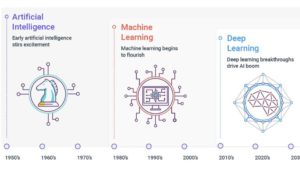
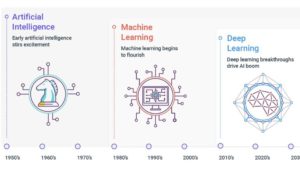
Does only AI make a good university?

Clker-Free-Vector-Images (CC0), Pixabay
Plans for a dedicated AI university campus in Bremen are causing a controversy. The plan is backed by a consortium of German software giant SAP, Chinese IT firm Neusoft and the German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence.
It is intended to take over the Jacobs University, a private university in the north of the city founded in 1999. The university has been funded up to now by the food company Jacobs, but they have announced they are ceasing their financial support. The university has always been controversial with questions over the need for a private university competing withe the state funded Bremen University.
THE reports that the Bremen government hopes that a dedicated AI campus will boost the local economy, attracting skilled workers and companies, although the city and firms involved have not yet drawn up detailed plans.
But there are fears from academics at Jacobs that the university, which sells itself on its interdisciplinary campus, will end up with too narrow a focus.
“AI is not necessarily a bad thing,” said Professor Bau. “The big question is: only AI, does that actually make a good university? Universities and university education are something that does not have a small focus.”



 UNESCO are increasingly active in the development in the use of Artificial Intelligence in Education. Next week – 7 and 8 of December they are hosting an International Forum on AI and the Futures of Education (AIED). The theme of the Forum is Developing Competencies for the AI Era. the Forum will bring togther education and technology experts from around the world to discuss AI skills for the futures of education and AI as a common good for education. UNESCO say participants will share policies and practices in defining the competencies required in the AI era, and examine strategies to prepare all people to live and work with AI effectively.
UNESCO are increasingly active in the development in the use of Artificial Intelligence in Education. Next week – 7 and 8 of December they are hosting an International Forum on AI and the Futures of Education (AIED). The theme of the Forum is Developing Competencies for the AI Era. the Forum will bring togther education and technology experts from around the world to discuss AI skills for the futures of education and AI as a common good for education. UNESCO say participants will share policies and practices in defining the competencies required in the AI era, and examine strategies to prepare all people to live and work with AI effectively.